Python, Tkinter, MSS를 사용한 화면 캡처 및 스코프 도구 만들기
Source: Dev.to
죄송합니다만, 해당 페이지의 전체 텍스트를 직접 가져올 수 없습니다. 번역을 진행하려면 번역하고자 하는 기사 본문을 여기 채팅창에 복사해 주시면, 코드 블록과 URL은 그대로 두고 마크다운 형식과 기술 용어를 유지하면서 한국어로 번역해 드리겠습니다.
실시간 화면 캡처 GUI와 스코프
이 튜토리얼에서는 실시간으로 화면을 캡처하고 비디오 스코프(벡터스코프, 히스토그램, 루마)를 표시하는 작은 GUI 도구를 만들겠습니다. 앱은 또한 관심 영역(ROI)을 선택하고, 색상을 샘플링하며, 비디오를 녹화할 수 있게 합니다.
단계 1 – 의존성 설치
pip install tkinter ttkbootstrap numpy mss opencv-python pillow| Library | 용도 |
|---|---|
| tkinter | 내장 GUI 프레임워크 |
| ttkbootstrap | 모던하고 스타일리시한 Tkinter 위젯 |
| numpy | 효율적인 수치 배열 |
| mss | 빠른 화면 캡처 |
| opencv‑python | 비디오 녹화 및 이미지 처리 |
| pillow | 이미지 처리 |
단계 2 – 메인 윈도우 만들기
import ttkbootstrap as tb
APP_TITLE = "Scopes – Screen Capture"
app = tb.Window(title=APP_TITLE, themename="darkly", size=(1280, 720))
app.grid_columnconfigure(1, weight=1) # make column 1 expandable
app.grid_rowconfigure(0, weight=1) # make row 0 expandablegrid_columnconfigure와 grid_rowconfigure는 창 크기를 조절할 때 캔버스가 확장되도록 합니다.
단계 3 – 컨트롤 및 뷰어 프레임 레이아웃
# Controls panel (left side)
controls = tb.Frame(app, padding=10)
controls.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="ns")
# Viewer panel (right side)
viewer = tb.Frame(app)
viewer.grid(row=0, column=1, sticky="nsew")
viewer.grid_columnconfigure(0, weight=1)
viewer.grid_rowconfigure(0, weight=1)
# Canvas for drawing scopes
import tkinter as tk
canvas = tk.Canvas(viewer, bg="black", highlightthickness=0)
canvas.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="nsew")캔버스는 벡터스코프, 히스토그램 및 루마 플롯을 표시합니다.
단계 4 – 시작/정지 및 녹화 버튼 추가
running = False
recording = False
def toggle_capture():
global running
running = not running
btn_start.config(text="Stop" if running else "Start")
btn_start = tb.Button(
controls,
text="Start",
bootstyle="success",
command=toggle_capture,
)
btn_start.pack(fill="x", pady=4)
def toggle_record():
global recording
recording = not recording
btn_rec.config(text="Stop REC" if recording else "Record")
btn_rec = tb.Button(
controls,
text="Record",
bootstyle="danger",
command=toggle_record,
)
btn_rec.pack(fill="x", pady=4)toggle_capture는 running 상태를 토글합니다.toggle_record는 recording 상태를 토글합니다.
단계 5 – 샘플링 및 게인 슬라이더 추가
tb.Label(controls, text="Sampling Step").pack(anchor="w")
sample_slider = tb.Scale(controls, from_=1, to=10, orient="horizontal")
sample_slider.set(4)
sample_slider.pack(fill="x")
tb.Label(controls, text="Gain").pack(anchor="w")
gain_slider = tb.Scale(controls, from_=1, to=10, orient="horizontal")
gain_slider.set(4)
gain_slider.pack(fill="x")슬라이더를 사용하면 사용자가 샘플링할 픽셀 수와 벡터스코프의 증폭 정도를 제어할 수 있습니다.
단계 6 – RGB를 YUV로 변환
import numpy as np
def rgb_to_yuv(rgb):
"""Convert an RGB image (0‑255) to YUV."""
r, g, b = rgb[..., 0], rgb[..., 1], rgb[..., 2]
y = 0.299 * r + 0.587 * g + 0.114 * b
u = -0.147 * r - 0.289 * g + 0.436 * b
v = 0.615 * r - 0.515 * g - 0.100 * b
return y, u, v스코프는 일반적으로 YUV 색 공간에서 시각화됩니다.
단계 7 – 캔버스에 스코프 그리기
def draw_scopes(frame):
"""Render vectorscope, RGB histogram and luma histogram on the canvas."""
canvas.delete("all")
h, w, _ = frame.shape
ch, cw = canvas.winfo_height(), canvas.winfo_width()
step = int(sample_slider.get())
gain = gain_slider.get()
small = frame[::step, ::step] / 255.0 # down‑sample & normalise
Y, U, V = rgb_to_yuv(small)
# ---------- VECTORSCOPE --------- Vectorscope – UV 평면에서 색 분포를 보여줍니다.
- RGB histogram – 채널별 강도 분포.
- Luma histogram – 밝기 분포.
단계 8 – 백그라운드 스레드에서 화면 캡처
import threading, time, mss, cv2
latest_frame = None
video_writer = None
FPS = 30
def capture_thread():
"""Continuously grab the screen, update `latest_frame`,
and write to a video file when recording."""
global latest_frame, video_writer
with mss.mss() as sct:
monitor = sct.monitors[1] # primary monitor
while True:
if running:
# Grab screen, drop the alpha channel
img = np.array(sct.grab(monitor))[:, :, :3]
latest_frame = img
# Write to video if recording
if recording:
h, w = img.shape[:2]
if video_writer is None:
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v")
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(
"capture.mp4", fourcc, FPS, (w, h)
)
video_writer.write(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
else:
# Stop and release writer when recording ends
if video_writer is not None:
video_writer.release()
video_writer = None
else:
# When not running, just sleep a bit
time.sleep(0.1)
# Refresh the canvas at the target FPS
if latest_frame is not None:
draw_scopes(latest_frame)
canvas.update_idletasks()
canvas.update()
time.sleep(1 / FPS)
# Start the capture thread
thread = threading.Thread(target=capture_thread, daemon=True)
thread.start()스레드:
- running이
True인 동안 화면을 캡처합니다. - 최신 프레임을
latest_frame에 저장합니다. - recording이
True일 때capture.mp4에 프레임을 기록합니다. - 원하는 프레임 속도로 GUI를 업데이트하기 위해
draw_scopes()를 호출합니다.
단계 9 – 애플리케이션 실행
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.mainloop()
Press **Start**를 눌러 실시간 캡처를 시작하고, **Record**를 눌러 비디오를 저장하며, 슬라이더를 조정하여 샘플링 밀도와 벡터스코프 게인을 변경합니다.
**실시간 스코프를 실험해 보세요!** 🎥✨캡처 스레드 시작
화면 캡처 및 스코프 도구 – 정리된 마크다운
Step 8: 비디오 프레임 쓰기 (선택 사항)
if video_writer is None:
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(
"recording.mp4",
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"),
FPS,
(w, h)
)
if video_writer.isOpened():
video_writer.write(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
time.sleep(1 / FPS)Step 9: UI 루프 업데이트
Tkinter는 메인 스레드에서 무거운 연산을 수행하는 것을 좋아하지 않으므로, 캔버스를 주기적으로 업데이트합니다:
def update_ui():
if running and latest_frame is not None:
draw_scopes(latest_frame)
app.after(33, update_ui) # ~30 FPS
update_ui()Step 10: ROI 및 색상 샘플링 추가
roi = None
start_pt = None
color_indicators = []
def on_mouse_down(e):
global start_pt
start_pt = (e.x_root, e.y_root)
def on_mouse_up(e):
global roi, start_pt
if not start_pt:
return
x1, y1 = start_pt
x2, y2 = e.x_root, e.y_root
roi = (min(x1, x2), min(y1, y2), max(x1, x2), max(y1, y2))
start_pt = None
canvas.bind("<ButtonPress-1>", on_mouse_down)
canvas.bind("<ButtonRelease-1>", on_mouse_up)
def on_key(e):
global roi
if e.keysym == "Escape":
app.destroy()
if e.keysym == "space":
import mss
x, y = app.winfo_pointerxy()
with mss.mss() as sct:
img = sct.grab(sct.monitors[1])
r, g, b = img.pixel(x, y)
color_indicators.append((r/255, g/255, b/255))
if e.keysym == "r":
roi = None
app.bind("<Key>", on_key)컨트롤
| 동작 | 키 / 마우스 |
|---|---|
| ROI 정의 (드래그) | 마우스 드래그 |
| 커서 위치 색상 샘플링 | Space |
| 종료 | Esc |
| ROI 초기화 | R |
Step 11: 애플리케이션 실행
app.mainloop()✅ 완료! 이제 Python으로 완전하게 동작하는 화면 캡처 및 스코프 도구를 갖게 되었습니다. 다음을 할 수 있습니다:
- 캡처 시작/중지
- 비디오 녹화
- 색상 분석
샘플링 속도와 게인을 조정하여 스코프를 미세 조정하세요.
예시 출력
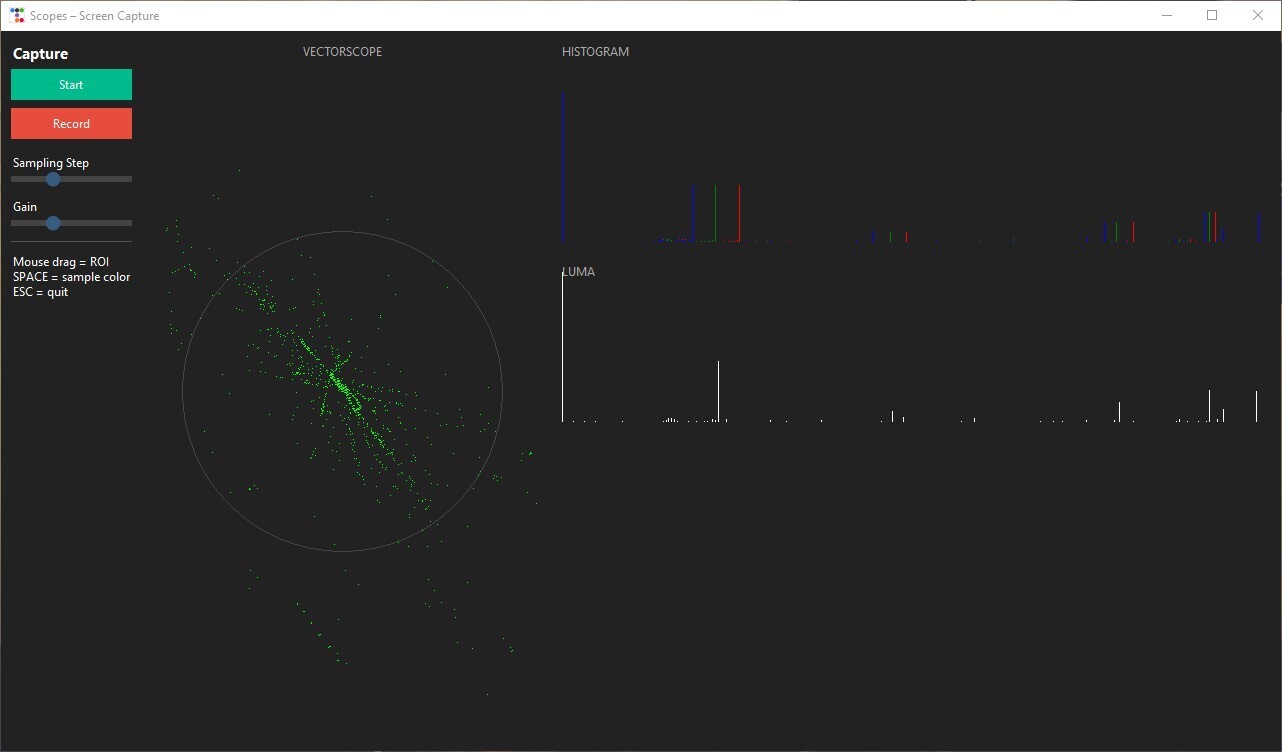 (이미지를 클릭하면 크게 볼 수 있습니다)
(이미지를 클릭하면 크게 볼 수 있습니다)