Unsloth와 함께 NVIDIA GPU에서 LLM을 파인튜닝하는 방법
Source: NVIDIA AI Blog
Modern workflows showcase the endless possibilities of generative and agentic AI on PCs.
Examples include tuning a chatbot to handle product‑support questions or building a personal assistant for managing one’s schedule. A challenge remains in getting a small language model to respond consistently with high accuracy for specialized agentic tasks.
That’s where fine‑tuning comes in.
Unsloth, one of the world’s most widely used open‑source frameworks for fine‑tuning LLMs, provides an approachable way to customize models. It’s optimized for efficient, low‑memory training on NVIDIA GPUs — from GeForce RTX desktops and laptops to RTX PRO workstations and DGX Spark, the world’s smallest AI supercomputer.
Another powerful starting point for fine‑tuning is the just‑announced NVIDIA Nemotron 3 family of open models, data, and libraries. Nemotron 3 introduces the most efficient family of open models, ideal for agentic AI fine‑tuning.
Teaching AI New Tricks
Fine‑tuning is like giving an AI model a focused training session. With examples tied to a specific topic or workflow, the model improves its accuracy by learning new patterns and adapting to the task at hand.
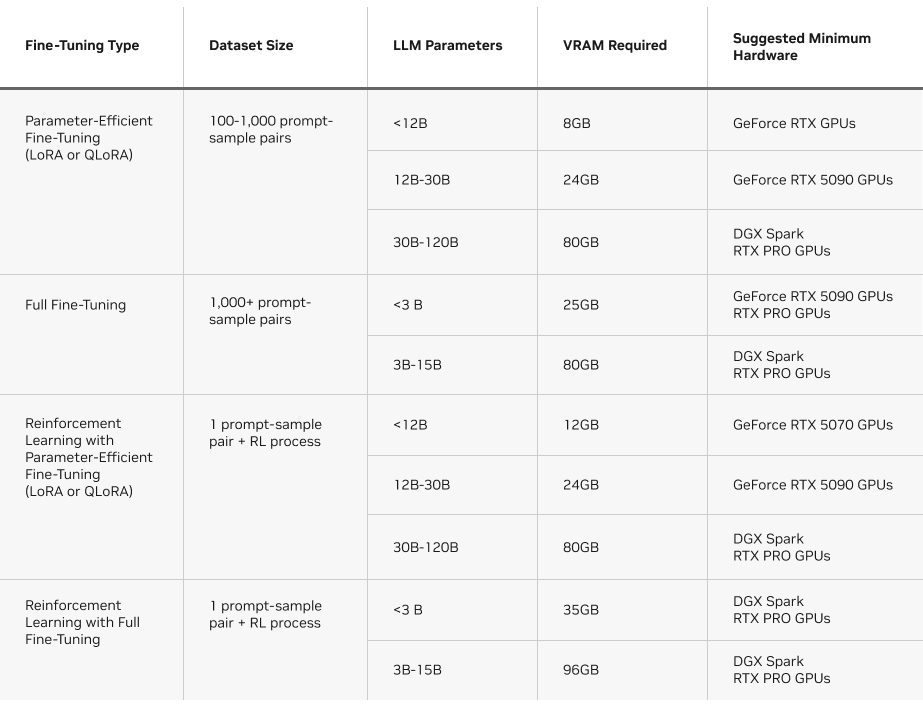
Choosing a fine‑tuning method depends on how much of the original model the developer wants to adjust. Based on their goals, developers can use one of three main fine‑tuning methods:
Parameter‑efficient fine‑tuning (e.g., LoRA or QLoRA)
- How it works: Updates only a small portion of the model for faster, lower‑cost training.
- Target use case: Useful across nearly all scenarios where full fine‑tuning would traditionally be applied — adding domain knowledge, improving coding accuracy, adapting the model for legal or scientific tasks, refining reasoning, or aligning tone and behavior.
- Requirements: Small‑ to medium‑sized dataset (100–1,000 prompt‑sample pairs).
Full fine‑tuning
- How it works: Updates all of the model’s parameters — useful for teaching the model to follow specific formats or styles.
- Target use case: Advanced use cases, such as building AI agents and chatbots that must provide assistance about a specific topic, stay within a certain set of guardrails, and respond in a particular manner.
- Requirements: Large dataset (1,000+ prompt‑sample pairs).
Reinforcement learning
- How it works: Adjusts the behavior of the model using feedback or preference signals. The model learns by interacting with its environment and uses the feedback to improve itself over time. This complex, advanced technique can be combined with parameter‑efficient or full fine‑tuning. See Unsloth’s Reinforcement Learning Guide for details.
- Target use case: Improving accuracy in a particular domain (e.g., law or medicine) or building autonomous agents that can orchestrate actions on a user’s behalf.
- Requirements: A process that contains an action model, a reward model, and an environment for the model to learn from.
Another factor to consider is the VRAM required per method. The chart below provides an overview of the requirements to run each type of fine‑tuning method on Unsloth.
Unsloth: A Fast Path to Fine‑Tuning on NVIDIA GPUs
LLM fine‑tuning is a memory‑and compute‑intensive workload that involves billions of matrix multiplications to update model weights at every training step. This heavy parallel workload requires the power of NVIDIA GPUs to complete quickly and efficiently.
Unsloth translates complex mathematical operations into efficient, custom GPU kernels to accelerate AI training. It boosts the performance of the Hugging Face Transformers library by ~2.5× on NVIDIA GPUs. These GPU‑specific optimizations, combined with Unsloth’s ease of use, make fine‑tuning accessible to a broader community of AI enthusiasts and developers.
The framework is built and optimized for NVIDIA hardware — from GeForce RTX laptops to RTX PRO workstations and DGX Spark — providing peak performance while reducing VRAM consumption. Unsloth also offers helpful guides, example notebooks, and step‑by‑step workflows.
Helpful guides
- Fine‑Tuning LLMs With NVIDIA RTX 50 Series GPUs and Unsloth
- Fine‑Tuning LLMs With NVIDIA DGX Spark and Unsloth
- Install Unsloth on NVIDIA DGX Spark
- NVIDIA technical blog: Train an LLM on a NVIDIA Blackwell desktop with Unsloth and scale it
For a hands‑on local fine‑tuning walkthrough, watch Matthew Berman demonstrating reinforcement learning on a NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 using Unsloth (video linked in the original article).
Available Now: NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Family of Open Models
The new Nemotron 3 family — Nano, Super, and Ultra sizes — is built on a hybrid latent Mixture‑of‑Experts (MoE) architecture, delivering the most efficient open‑model lineup with leading accuracy, ideal for agentic AI applications.
- Nemotron 3 Nano 30B‑A3B (available now) is the most compute‑efficient model, optimized for software debugging, content summarization, AI‑assistant workflows, and information retrieval at low inference cost. Its hybrid MoE design delivers:
- Up to 60 % fewer reasoning tokens, significantly reducing inference cost.
- A 1 million‑token context window, enabling far more information retention for long, multistep tasks.
- Nemotron 3 Super is a high‑accuracy reasoning model for multi‑agent applications.
- Nemotron 3 Ultra targets complex AI applications. Both are expected in the first half of 2026.
NVIDIA also released an open collection of training datasets and state‑of‑the‑art reinforcement‑learning libraries. Nemotron 3 Nano fine‑tuning is available on Unsloth.
- Download Nemotron 3 Nano from Hugging Face
- Experiment with it via Llama.cpp and LM Studio
DGX Spark: A Compact AI Powerhouse
DGX Spark enables local fine‑tuning and delivers incredible AI performance in a compact desktop supercomputer, giving developers access to more memory than a typical PC.
Built on the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell architecture, DGX Spark provides up to a petaflop of FP4 AI performance and includes 128 GB of unified CPU‑GPU memory, offering headroom to run larger models, longer context windows, and more demanding training workloads locally.
For fine‑tuning, DGX Spark enables:
- Larger model sizes: Models with >30 billion parameters often exceed the VRAM capacity of consumer GPUs but fit comfortably within DGX Spark’s unified memory.
- More advanced techniques: Full fine‑tuning and reinforcement‑learning workflows become feasible thanks to the abundant memory and compute resources.