UC San Diego Lab Advances Generative AI Research With NVIDIA DGX B200 System
Source: NVIDIA AI Blog
December 17, 2025 by Zoe Kessler

How Is Hao AI Lab Using the DGX B200?
Members of the Hao AI Lab standing with the NVIDIA DGX B200 system.
With the DGX B200 now fully accessible to the Hao AI Lab and the broader UC San Diego community at the School of Computing, Information and Data Sciences’ San Diego Supercomputer Center, the research opportunities are boundless.
“DGX B200 is one of the most powerful AI systems from NVIDIA to date, which means that its performance is among the best in the world,” said Hao Zhang, assistant professor in the Halıcıoğlu Data Science Institute and Department of Computer Science and Engineering at UC San Diego. “It enables us to prototype and experiment much faster than using previous‑generation hardware.”
Projects accelerated by the DGX B200
-
FastVideo – Trains a family of video‑generation models that can produce a five‑second video from a text prompt in five seconds. The research phase also leverages NVIDIA H200 GPUs alongside the DGX B200.
-
Lmgame‑bench – A benchmarking suite that pits large language models (LLMs) against popular online games such as Tetris and Super Mario Bros. Users can evaluate a single model or pit two models against each other to compare performance.
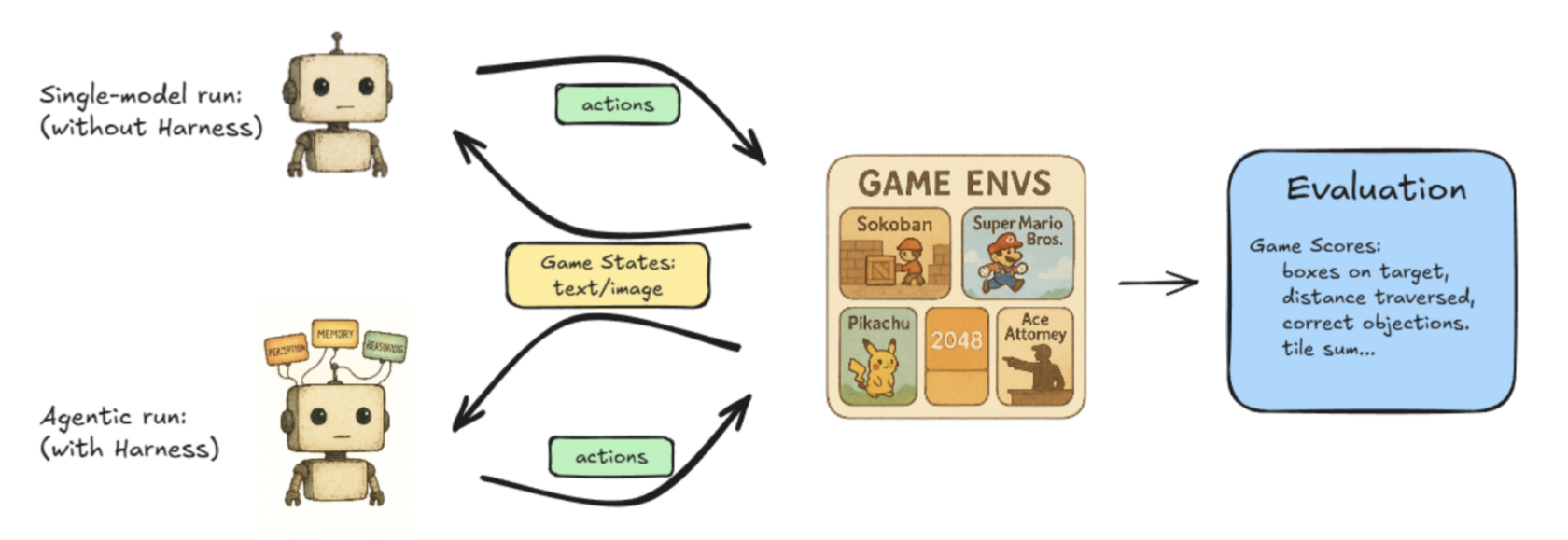
The illustrated workflow of Hao AI Lab’s Lmgame‑Bench project. -
Low‑latency LLM serving – Ongoing work explores new techniques for delivering real‑time responsiveness from large language models.
“Our current research uses the DGX B200 to explore the next frontier of low‑latency LLM‑serving on the awesome hardware specs the system gives us,” said Junda Chen, a doctoral candidate in computer science at UC San Diego.
How DistServe Influenced Disaggregated Serving
Disaggregated inference enables large‑scale LLM‑serving engines to maximize aggregate system throughput while keeping user‑perceived latency within acceptable bounds.
Why Disaggregated Inference Matters
- Optimizes “goodput” rather than raw throughput.
- Aligns system performance with real‑world user experience.
Throughput vs. Goodput
| Metric | Definition | What It Captures | Trade‑off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Number of tokens generated per second by the whole system. | Cost efficiency (tokens / $). | Ignores latency; higher throughput can increase user‑perceived delay. |
| Goodput | Throughput while meeting user‑specified latency objectives (SLOs). | Both cost efficiency and service quality. | Balances speed with responsiveness, giving a more holistic view of system health. |
Key Takeaways
- Throughput alone is insufficient because it does not reflect the latency users experience.
- Goodput incorporates latency constraints, making it a superior metric for LLM‑serving workloads.
- By focusing on goodput, DistServe achieves optimal efficiency and ideal model output without sacrificing user experience.
How Can Developers Achieve Optimal Goodput?
When a user makes a request in an LLM system, the system takes the user input and generates the first token (the prefill). Then it creates numerous output tokens, one after another, predicting each token’s future behavior based on past requests’ outcomes. This process is known as decode.
Historically, prefill and decode have run on the same GPU, but the researchers behind DistServe found that splitting them onto different GPUs maximizes goodput.
“Previously, if you put these two jobs on a GPU, they would compete with each other for resources, which could make it slow from a user perspective,” Chen said. “Now, if I split the jobs onto two different sets of GPUs — one doing prefill, which is compute‑intensive, and the other doing decode, which is more memory‑intensive — we can fundamentally eliminate the interference between the two jobs, making both jobs run faster.”
This process is called prefill/decode disaggregation, or separating the prefill from decode to get greater goodput.
- Increasing goodput and using the disaggregated inference method enables continuous scaling of workloads without compromising low latency or high‑quality model responses.
- NVIDIA Dynamo – an open‑source framework designed to accelerate and scale generative AI models at the highest efficiency levels with the lowest cost – enables scaling disaggregated inference.
In addition to these projects, cross‑departmental collaborations (e.g., in healthcare and biology) are underway at UC San Diego to further optimize a range of research projects using the NVIDIA DGX B200, as researchers continue exploring how AI platforms can accelerate innovation.
Learn more about the NVIDIA DGX B200 system.
Categories & Tags
Categories:
Tags:
Related NVIDIA News
Stay tuned for more updates on NVIDIA’s AI innovations and research breakthroughs.




