SageMaker Unified Studio: Your All-in-One AWS Analytics Platform
Source: Dev.to
Overview
SageMaker Unified Studio (later we’ll use SUS as the abbreviation) can feel confusing if you come from the traditional, individual AWS analytical services—because it wraps all the services you already know:
| Service | Purpose |
|---|---|
| S3 | Storage |
| Lake Formation | Data governance with fine‑grained permissions |
| Glue | Spark workloads & data‑catalog management |
| Redshift | Data warehouse |
| Athena | Ad‑hoc SQL queries |
| SageMaker Notebook | Running Python scripts or connecting to Glue Interactive Sessions |
| Bedrock | Generative & agentic AI components |
| Amazon Q | AI‑assisted code generation (SQL & Python) |
| DataZone | Business catalog, project management, cross‑domain data sharing |
| EMR | Big‑data processing with Spark |
These components add operational and governance overhead for data, compute, and security, and they often exist in silos.
Why a Lakehouse Architecture?
The Problem
You might wonder why we’re even talking about lakehouse architecture. It solves a massive pain point you’ve probably experienced.
The Traditional Mess We’ve All Dealt With
Scenario 1 – The Data Lake Approach
- Dump all data into S3 (cheap storage ✅)
- Need to run analytics…
- Performance is terrible ❌
- No ACID transactions ❌
- Data‑quality enforcement? Good luck! ❌
Result: Copy data to Redshift for actual analytics.
Scenario 2 – The Data Warehouse Approach
- Load everything into Redshift (great performance ✅)
- Storage costs skyrocket 💸
- Can’t handle semi‑structured data well ❌
- ML teams want raw data in S3 anyway ❌
Result: Maintain both S3 and Redshift with duplicate data.
The Real Problems
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Data duplication | Paying for the same data multiple times |
| Complex ETL pipelines | Moving data between systems |
| Multiple permission models | Managing security across services |
| Inconsistent data | Trust issues |
| Slow time‑to‑insight | Overhead delays |
| High operational costs | Duplicate infrastructure |
Sound familiar? This is exactly why SageMaker Unified Studio provides a unified platform to implement lakehouse architecture.
The Solution: Lakehouse Architecture
Lakehouse architecture combines the best of both worlds:
Data Lake + Data Warehouse = Lakehouse
“A data lakehouse is an architecture that unifies the scalability and cost‑effectiveness of data lakes with the performance and reliability characteristics of data warehouses. This approach eliminates the traditional trade‑offs between storing diverse data types and maintaining query performance for analytical workloads.” — AWS documentation
Key Benefits
- ✅ Transactional consistency – ACID compliance for reliable concurrent operations
- ✅ Schema management – Flexible schema evolution without breaking existing queries
- ✅ Compute‑storage separation – Independent scaling of processing and storage resources
- ✅ Open standards – Compatibility with the Apache Iceberg table format
- ✅ Single source of truth – Eliminates data silos and redundant storage costs
- ✅ Real‑time & batch processing – Supports streaming and historical analytics
- ✅ Direct file access – Enables both SQL queries and programmatic data access
- ✅ Unified governance – Consistent security & compliance across all data types
This architectural approach is what SageMaker Unified Studio helps you implement without the usual complexity.
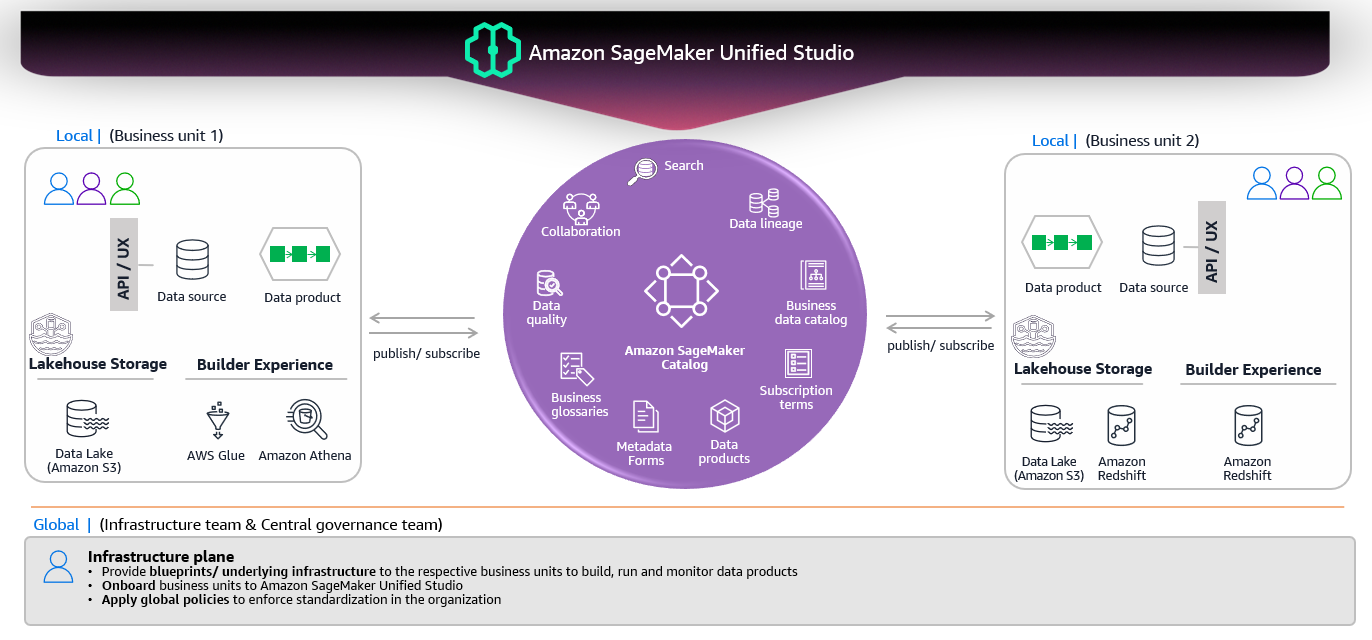
How SageMaker Unified Studio Implements a Lakehouse
According to AWS documentation:
“The lakehouse architecture of Amazon SageMaker unifies data across Amazon S3 data lakes and Amazon Redshift data warehouses so you can work with your data in one place.”
1. Unified Data Access Through a Single Catalog
Instead of juggling separate connections to S3, Redshift, Aurora, DynamoDB, etc., you get one unified interface:
- AWS Glue Data Catalog – The single catalog where you discover and query all data.
- Apache Iceberg – Open table format that provides interoperability across analytics engines.
- Multiple query engines (Athena, Redshift, Spark on EMR) can all access the same data without duplication.
How it works:
“When you run a query, AWS Lake Formation checks your permissions while the query engine processes data directly from its original storage location, whether that’s Amazon S3 or Amazon Redshift.”
Result: Data stays where it is—no unnecessary movement or duplication.
2. Two Types of Data Access
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Managed Data Sources | • Amazon S3 data lakes – Including S3 tables with built‑in Apache Iceberg support. • Amazon Redshift – Query directly against Redshift tables. |
| External Data Sources | • Amazon Aurora, DynamoDB, RDS, etc. – Accessed via federated queries or connectors, still governed by Lake Formation. |
Both managed and external sources are governed by a single permission model (Lake Formation), simplifying security and compliance.
3. Compute‑Storage Separation
- Storage – Remains in S3 (or Redshift) and is never duplicated.
- Compute – You can spin up Athena, EMR Spark, Redshift Serverless, or SageMaker Processing jobs on‑demand, scaling independently of storage.
4. Unified Governance
- Lake Formation enforces fine‑grained access controls across all data, regardless of where it lives.
- DataZone provides a business‑level catalog and project‑level permissions, ensuring that the right teams see the right data.
5. End‑to‑End Workflow (Simplified)
- Ingest raw data into S3 (or stream into a Delta/Iceberg table).
- Register the table in the Glue Data Catalog (automatically picks up Iceberg metadata).
- Set Lake Formation permissions for users, groups, or roles.
- Query via Athena, Redshift, or Spark—no ETL needed to move data.
- Consume results in SageMaker notebooks, SageMaker Studio, or downstream ML pipelines.
Takeaway
- SageMaker Unified Studio removes the silos that traditionally force you to maintain separate data lakes and warehouses.
- By leveraging Lake Formation, Glue Data Catalog, and Apache Iceberg, SUS gives you a true lakehouse—single source of truth, ACID‑compliant, and governed uniformly.
- The result is lower costs, simpler operations, faster time‑to‑insight, and consistent security across all your analytical workloads.
Additional Capabilities
- Redshift warehouse tables – Accessible as Iceberg tables through Redshift Spectrum
- Zero‑ETL destinations – Near real‑time data replication from:
- SaaS sources (Salesforce, SAP, Zendesk)
- Operational databases (Amazon Aurora, Amazon RDS for MySQL)
- NoSQL databases (Amazon DynamoDB)
Federated Data Sources (Query in‑place without moving data)
- Operational databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server)
- AWS‑managed databases (Amazon Aurora, Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon DocumentDB)
- Third‑party data warehouses (Snowflake, Google BigQuery)
When you connect federated sources in SUS, AWS automatically provisions the required infrastructure components (AWS Glue connection, Lambda functions) that act as bridges between the query engines and the federated data source.
Centralized Governance with Lake Formation
One permission model (AWS Lake Formation) that enforces access control consistently across:
- S3 data lakes
- Redshift data warehouses
- Federated sources
- All query engines (Athena, Redshift Query Editor v2, EMR, Glue)
Fine‑grained control at table, column, row, and cell levels—defined once, enforced everywhere.
Project‑Based Organization with DataZone
Amazon DataZone powers the project and domain management in SUS:
- Business catalog – data discovery and data‑product publishing
- Project boundaries – collaboration and permissions
- Cross‑domain data sharing – governed data access across teams
- Domain management – organizing multiple projects
Architecture Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lakehouse Architecture | Architectural pattern/approach (not a product) |
| SageMaker Unified Studio | Unified platform that implements lakehouse architecture |
| Athena, Redshift, Spark (EMR) | Query/compute engines that process your queries |
| Glue Data Catalog | Unified metadata catalog (single source of truth for metadata) |
| Lake Formation | Governance layer providing fine‑grained permissions |
| DataZone | Business catalog and project‑management layer |
| Apache Iceberg | Open table format enabling cross‑engine interoperability |
Now that you understand how SUS implements lakehouse architecture, let’s see how it organizes your workflow.
The Three Core Sections of SUS
With lakehouse architecture providing unified data access, SUS organizes your workflow into three intuitive sections:
A. Discover
Your starting point for data exploration:
- Data Catalog (powered by AWS Glue Data Catalog) – discover all available data across lakes, warehouses, and federated sources
- Business Catalog (powered by DataZone) – find published data products and datasets shared across domains
- Bedrock Playground – experiment with generative AI models and prompts
This is where you explore what data is available across all your sources—all unified through the single catalog.
B. Build
This is where the action happens. SUS provides access to multiple analytical and ML tools:
Query Editors
- Amazon Athena Query Editor – serverless SQL queries across S3 and federated sources
- Amazon Redshift Query Editor v2 – high‑performance queries on warehouse data
Notebooks & Development
- JupyterLab Notebooks – data science, ML development, and programmatic data access
- SageMaker Training – building and training ML models
- SageMaker Inference – deploying models
Data Processing
- AWS Glue Visual ETL – no‑code/low‑code data transformations
- Amazon EMR – big‑data processing with Apache Spark
Orchestration
- Amazon MWAA (Airflow) – workflow orchestration and scheduling
AI Assistance
- Amazon Q Developer – AI‑assisted SQL and Python code generation
All these tools access your unified data seamlessly through different query engines, without requiring data movement.
C. Govern
Making your curated and valuable data consumable for other consumers:
- Publish data products to the business catalog
- Share datasets across projects and domains
- Enforce permissions consistently through Lake Formation
- Track data lineage and usage
- Manage data quality and compliance
Lake Formation ensures consistent permissions across all access patterns and query engines, while DataZone manages the business metadata and sharing workflows.
Understanding the Architecture

The different green boxes represent the concepts of SageMaker Unified Studio and how they interconnect:
| From | To | Relationship | Cardinality | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Domain units | contains | 1 : M | Organizational structure |
| Domain | Projects | consist of | 1 : M | Projects belong to a domain |
| Projects | Users | include members | M : M | Users work in projects |
| Projects | Data | encapsulate | 1 : M | Projects access data sources |
| Users | Assets | govern data via | M : M | Users create/manage assets |
| Data | Assets | is published into | M : M | Data curated into assets |
The green boxes together represent the DataZone‑powered organizational framework that provides:
- ✅ Structure – Domain, Domain units
- ✅ Collaboration – Projects, Users
- ✅ Data management – Data, Assets
- ✅ Governance – Permissions flow through all six elements
This is the foundation that enables lakehouse architecture implementation in SageMaker Unified Studio!
Summary
SUS provides the platform layer that implements lakehouse architecture, with the unified catalog at the center and multiple query engines accessing data from lakes, warehouses, and federated sources—all governed consistently through Lake Formation and organized via DataZone.
## 🚀 Try It Yourself
Want hands‑on experience? AWS offers a practical workshop that covers everything discussed in this post:
**👉 [SageMaker Unified Studio Workshop](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/1e711c46-2bda-4c72-9f62-fde6347800f8/en-US)**
This workshop simulates a real‑world scenario from the perspective of different data professionals tackling actual business challenges. You’ll walk through the end‑to‑end process—from initial data analysis to deploying a GenAI‑powered, tailored student‑engagement solution.
**Read the workshop and follow the screenshots to understand SUS and the workshop implementation.**💬 Feedback Welcome
What did you think?
- ✅ Helpful sections?
- 🤔 Confusing parts?
- 💡 Topics for the next post?
Have you tried SageMaker Unified Studio? Share your experience in the comments!