Optimizing AWS Lambda Performance: Balancing Power and Cost
Source: Dev.to
Over the past week I ran a series of performance tests to fine‑tune an AWS Lambda function’s configuration, focusing on the balance between execution speed and cost efficiency.
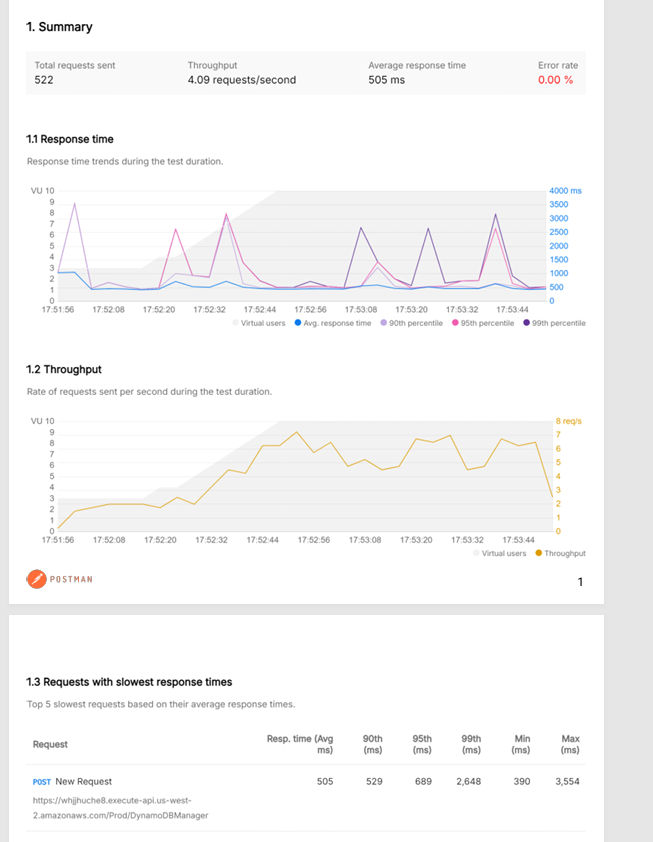
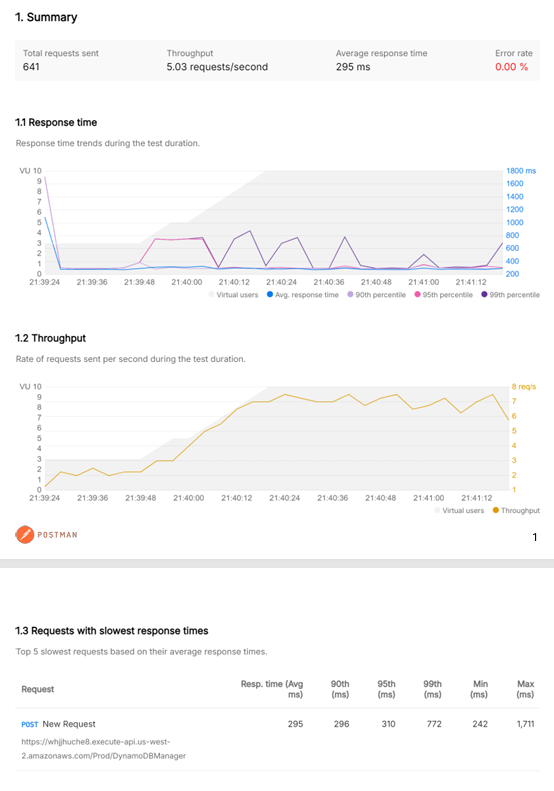
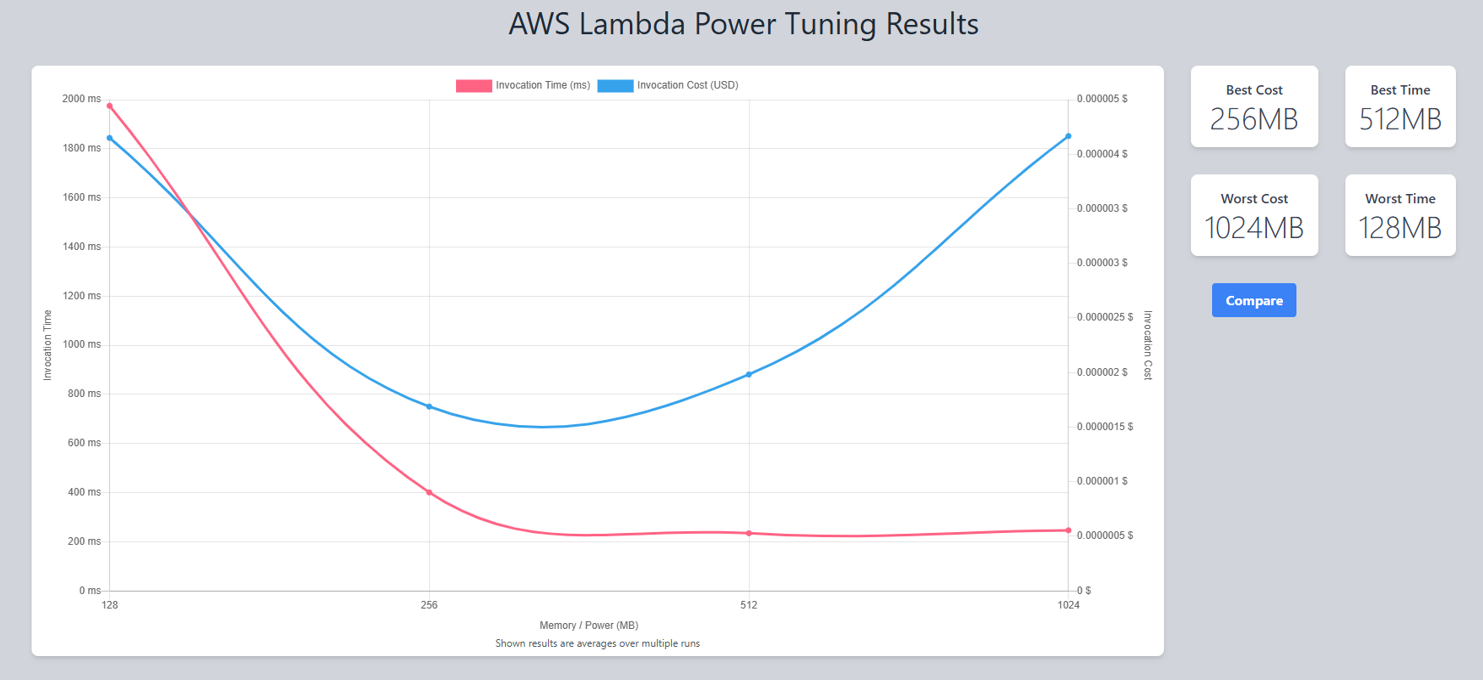
Using AWS Lambda Power Tuning, I tested the function with memory allocations of 128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB, and 1024 MB. Each configuration was then load‑tested with Postman’s Performance Testing feature to simulate concurrent requests and measure throughput, latency, and stability.
Test Configurations and Results
| Memory | Avg. Latency | Throughput (req/sec) | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128 MB | > 1 s | – | 0 % |
| 256 MB | Improved, still noticeable lag at high concurrency | – | 0 % |
| 512 MB | ≈ 505 ms | 4.09 | 0 % |
| 1024 MB | ≈ 295 ms | 5.03 | 0 % |
All tests completed successfully with a 0 % error rate, confirming stable performance across configurations.
Key Takeaways
- Increasing Lambda memory allocation also boosts the available CPU power, reducing execution time.
- Higher memory incurs a higher cost per invocation, so the goal is to find the “sweet spot” where performance gains justify the extra expense.
- In this scenario, 512 MB offered a strong balance between speed and cost, while 1024 MB delivered maximum performance for latency‑sensitive workloads.
- Combining AWS Lambda Power Tuning with Postman Load Testing enables data‑driven decisions that optimize both performance and cost efficiency in serverless applications.